- What is ¡®Nuclear Medicine¡¯
Nuclear medicine procedures use pharmaceuticals that have been labeled with radionuclides (radiopharmaceuticals). In diagnosis, radioactive substances are administered to patients and the radiation emitted is detected. The diagnostic tests involve the formation of an image using a gamma camera or positron emission tomography. Also radioiodine therapy is using for differentiated thyroid cancer or thyrotoxicosis
- In vivo diagnostic images
1) Bone scan
The more active the bone turnover, the more radioactive material will be seen. The bone scan can detect the bone lesions more sensitive and earlier than other bone imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray and computed tomography (CT).

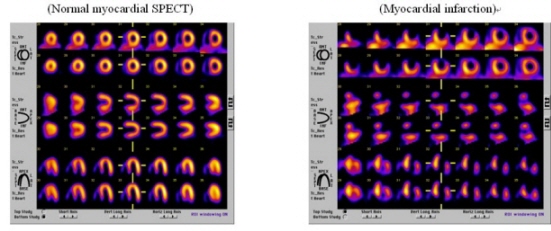
2) Myocardial perfusion SPECT
Myocardial perfusion SPECT is a form of functional cardiac imaging, used for the diagnosis of ischemic heart disease. The underlying principle is that under conditions of stress, diseased myocardium receives less blood flow than normal myocardium.
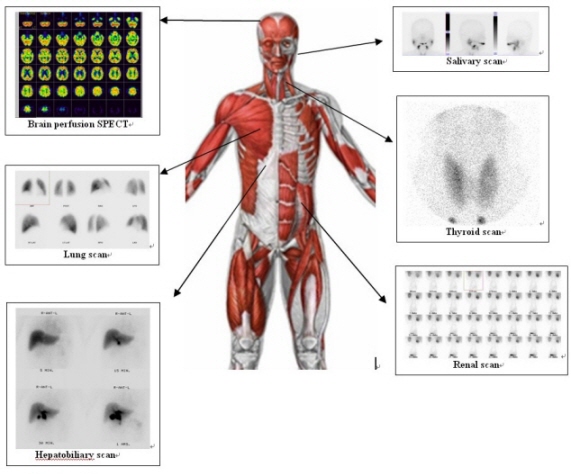
3) Other nuclear images
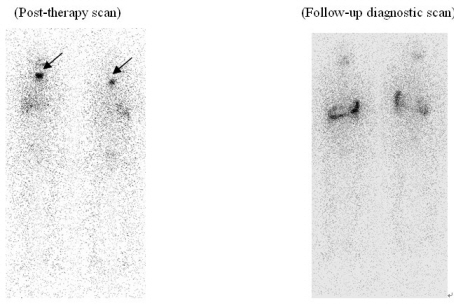
- Radioiodine therapy
Oral administration of iodine-131is used to treatment of thyroid cancer or thyrotoxicosis. Radioiodine therapy is useful method to ablation of remnant thyroid tissue or metastatic lesions after total thyroidectomy on well differentiated thyroid carcinoma such as papillary or follicular type.
(Example)56 year-old female patient with papillary thyroid cancer underwent total thyroidectomy. High dose radioiodine therapy (150mCi) were performed and there were remnant thyroid tissue uptake on post-therapy scan (arrow). After 6 months, the remnant thyroid tissue was all disappeared with no significant iodine uptakes in diagnostic I-131 scan.
- Most advanced Positron Emission Tomography (PET/CT)
1)What is PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
PET is the most advanced visual inspection that allows direct observation of the systematic metabolism by injecting the combination of the substance used in the metabolism of body such as dextrose and radioactive material that emits the positron. Because of the most diseases including cancer cause changes in metabolism before any structural changes occur, PET is able to detect diseases in the earlier stage than other tests.
2)What is PET/CT
Although PET is a detailed test that allows direct observation of the systematic metabolism, it has been difficult to identify the correct location of the focus. In order to overcome such disadvantage, PET is combined with CT that provides more structural information, so that the changes in metabolism and structure are simultaneously observed and the accuracy of the test is enhanced.
PET/CT is the most advanced visual diagnosis that determines the accurate location and size of the focus by identifying metabolic changes observed by PET in CT image at the same time

3)Cases when PET/CT is required
1.
Early detection of cancer, discernment of transition stage and exact location
2.
Nervous system disease
3.
Heart disease
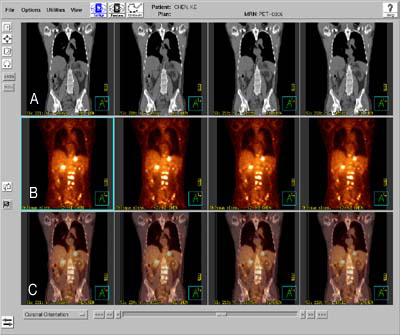
(A: CT image, B: PET image, C: Fusion image with CT and PET, Bright uptake lesion on B and C showed metastasis from cancer)
4)PET/CT test process
2. Injection of radioactive medication
3. Standby (1 hour): PET/CT rest room, urinate just prior to test
4. PET/CT (30-40 minutes): Radiographic room